

In general, a return loss of 15 dB or better is considered an acceptable overall return loss for a cable and antenna system.

In contrast, VSWR is a linear measurement and helps measure larger reflections. The primary difference between return loss and VSWR is that return loss is a logarithmic measurement, making it useful when measuring very small reflections. Return loss and VSWR are important metrics of RF interconnect system performance. These high-power connectors can be used with foam or air dielectric cables.
Swept right angle sma connector series#
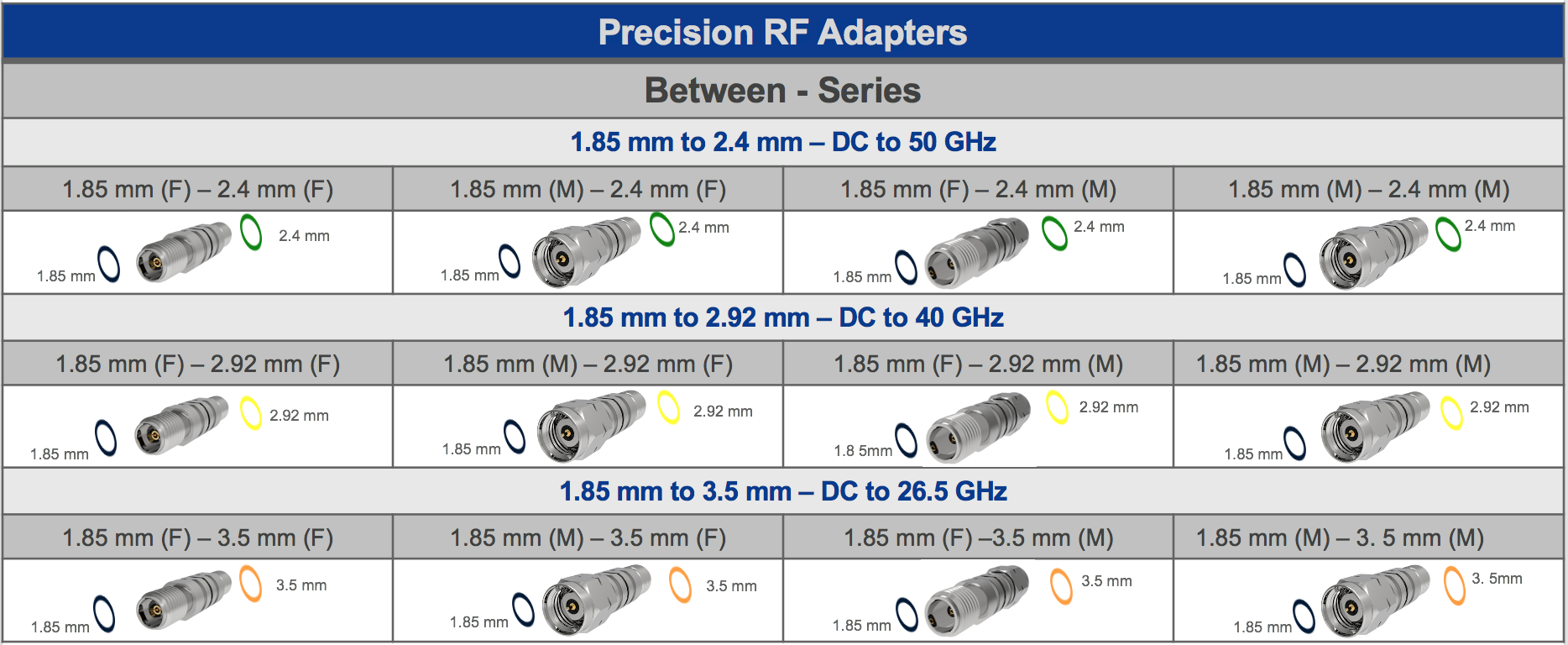
They use an M29 x 1.5 threaded coupling nut.ĮIA series coaxial connectors come in a variety of sizes, including EIA 7/8”, EIA 1 5/8”, EIA 3 1/8”, EIA 4 1/2”, and EIA 6 1/8”. These connectors have an inner conductor with a diameter of 7 mm and an outer conductor with a diameter of 16 mm. There are versions with threaded collars for a more secure connection, like TNC connectors.ħ-16 DIN connectors have largely replaced C-type connectors, and can handle somewhat higher power levels. Standard C-type connectors are rated for 50 Ω, but 75 Ω designs are also available. They can be used at all K-band frequencies.Ĭ-type connectors use a bayonet retention collar similar to BNCs but are designed to handle much higher power levels. They have limited power-handling capability.Ģ.92mm / K type connectors have similar performance to 2.4mm designs, but are limited to 40 GHz. 3.5mm connectors tend to have lower power ratings compared with SMA connectors.Ģ.4mm connectors are rated to 50 GHz and are available in three grades general-purpose, instrumentation, and metrology. They can handle power levels between BNC and TNC connectors.ģ.5mm connectors are precision designs similar to an SMA connector but with an air dielectric that supports frequencies up to 34 GHz.

SMA, sub-miniature type A, connectors are rated for up to 18 GHz, with precision designs rated up to 26.5 GHz. Like BNC connectors, N connectors are available with characteristic impedances of 50 or 75 Ω. Standard versions are rated for 11 GHz, with precision designs capable of operating to 18 GHz. The threads provide a more solid connection that can withstand vibrations and handle higher frequencies and power levels than BNCs. TNC connectors are threaded versions of a BNC connector. BNC connectors are typically rated for 500V and about 100W average power up to about 1 GHz however, they are most commonly used at 500 MHz and below. (Image: A R RF/Microwave Instrumentation)Ī few of the common connector types used in RF applications include:īNC connectors are inexpensive, include a locking mechanism to prevent unintentional disconnection, and are available with characteristic impedances of 50 or 75 Ω. Figure 1: Typical power and frequency handling capabilities of representative RF connectors. A connector’s physical size, frequency range, and power handling capabilities are interrelated (Figure 1). Six keys to selecting and integrating GHz connectors include physical size, frequency range capabilities, power handling, voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) and return loss, passive intermodulation distortion (PIM), and controlling unwanted electromagnetic interference (EMI). Designers have a broad range of connectors to choose from, but there are a few key parameters to consider when narrowing down the choices.
Connectors are essential components in radio frequency (RF) systems, especially in high-frequency applications like Gigahertz (GHz) 5G devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
